
 The use of fly ash in various applications is governed by a range of standards and regulations at both international and regional levels. These standards aim to ensure the quality, performance, and safety of fly ash in its intended uses. At the international level, ASTM C618 in the United States and EN 450 in Europe are prominent standards for fly ash used in concrete. ASTM C618 specifies the chemical and physical requirements for Class F and Class C fly ash, including limits on fineness, loss on ignition (LOI), and pozzolanic activity. EN 450, on the other hand, includes categories based on fineness and LOI and sets limits for various chemical properties relevant to concrete performance. These international standards provide a critical benchmark for the quality of fly ash used in construction across different regions.
The use of fly ash in various applications is governed by a range of standards and regulations at both international and regional levels. These standards aim to ensure the quality, performance, and safety of fly ash in its intended uses. At the international level, ASTM C618 in the United States and EN 450 in Europe are prominent standards for fly ash used in concrete. ASTM C618 specifies the chemical and physical requirements for Class F and Class C fly ash, including limits on fineness, loss on ignition (LOI), and pozzolanic activity. EN 450, on the other hand, includes categories based on fineness and LOI and sets limits for various chemical properties relevant to concrete performance. These international standards provide a critical benchmark for the quality of fly ash used in construction across different regions.
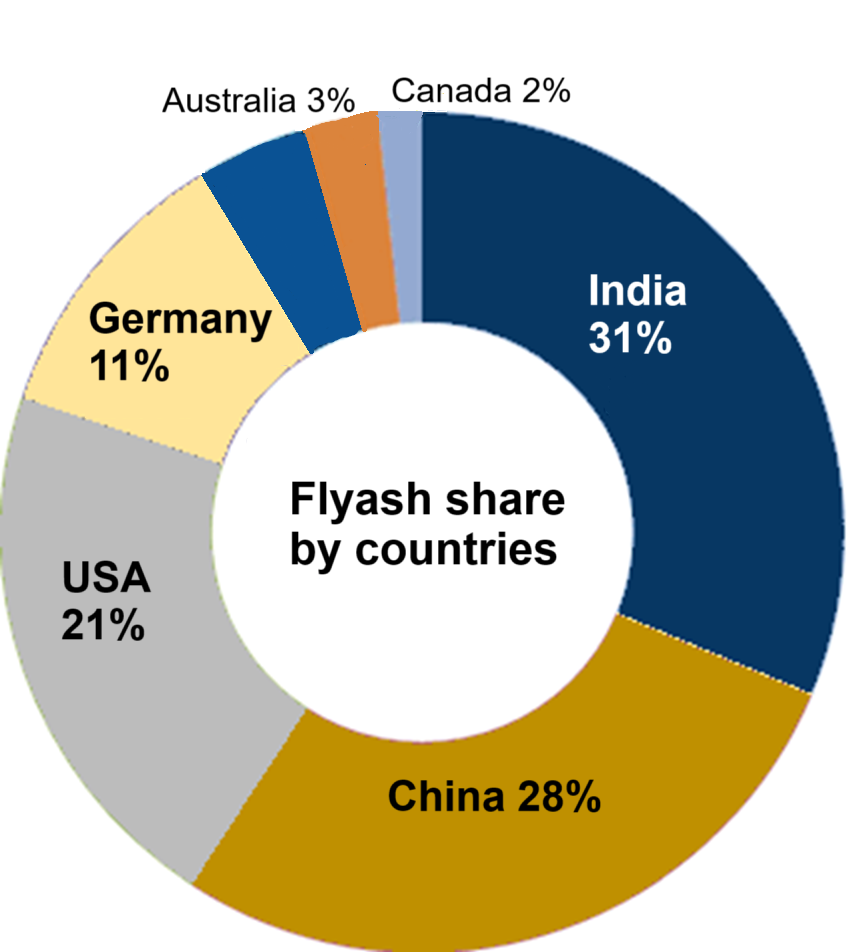 Regionally, countries like India, China, and Australia have developed their own standards and guidelines for fly ash utilization. In India, IS 3812 covers fly ash for use as pozzolana and admixture, while IS 12894 specifies requirements for fly ash-lime bricks. China has an extensive system of national, industrial, and local standards, including GB/T 1596 and DL/T 2297-2021, addressing the use of fly ash in cement, concrete, and other applications. Australia's AS 3582.1 specifies requirements for fly ash as a supplementary cementitious material, defining different grades based on physical properties. These regional standards often align with international frameworks but may include specific requirements tailored to local conditions and coal characteristics. Across these various standards, there are common specific requirements that fly ash must meet. These typically include limits on chemical composition, such as the minimum combined content of SiO2, Al2O3, and Fe2O3, as well as maximum limits for CaO, MgO, SO3, and alkalis. Fineness, usually measured by sieve analysis, is another key requirement related to the reactivity and workability of fly ash. The loss on ignition (LOI) is also regulated to control the amount of unburned carbon, which can have adverse effects on concrete properties. Additionally, a pozzolanic activity index is often specified to ensure the reactivity of the fly ash when used with Portland cement. Fly ash is widely used in the production of both blended cements and as a direct addition to concrete mixes. Standards like ASTM C618 and EN 450 provide guidelines for its use in concrete, considering its impact on workability, strength, and durability. Fly ash is also a key component in Portland pozzolana cement (PPC), where it is interground or blended with Portland cement clinker, as outlined in standards like IS 1489 and BS 6610. The content of fly ash in PPC is often specified within these standards to ensure the desired performance characteristics of the cement.
Regionally, countries like India, China, and Australia have developed their own standards and guidelines for fly ash utilization. In India, IS 3812 covers fly ash for use as pozzolana and admixture, while IS 12894 specifies requirements for fly ash-lime bricks. China has an extensive system of national, industrial, and local standards, including GB/T 1596 and DL/T 2297-2021, addressing the use of fly ash in cement, concrete, and other applications. Australia's AS 3582.1 specifies requirements for fly ash as a supplementary cementitious material, defining different grades based on physical properties. These regional standards often align with international frameworks but may include specific requirements tailored to local conditions and coal characteristics. Across these various standards, there are common specific requirements that fly ash must meet. These typically include limits on chemical composition, such as the minimum combined content of SiO2, Al2O3, and Fe2O3, as well as maximum limits for CaO, MgO, SO3, and alkalis. Fineness, usually measured by sieve analysis, is another key requirement related to the reactivity and workability of fly ash. The loss on ignition (LOI) is also regulated to control the amount of unburned carbon, which can have adverse effects on concrete properties. Additionally, a pozzolanic activity index is often specified to ensure the reactivity of the fly ash when used with Portland cement. Fly ash is widely used in the production of both blended cements and as a direct addition to concrete mixes. Standards like ASTM C618 and EN 450 provide guidelines for its use in concrete, considering its impact on workability, strength, and durability. Fly ash is also a key component in Portland pozzolana cement (PPC), where it is interground or blended with Portland cement clinker, as outlined in standards like IS 1489 and BS 6610. The content of fly ash in PPC is often specified within these standards to ensure the desired performance characteristics of the cement.